Quick Start
One page summary of how to start a new FTL project.
Requirements
Install the FTL CLI
Install the FTL CLI on Mac or Linux via Homebrew, Hermit, or manually.
- Homebrew
- Hermit
- Manually
brew tap block/ftl && brew install ftl
FTL can be installed from the main Hermit package repository by simply:
hermit install ftl
Alternatively you can add hermit-ftl to your sources by adding the following to your Hermit environment's bin/hermit.hcl file:
sources = ["https://github.com/block/hermit-ftl.git", "https://github.com/cashapp/hermit-packages.git"]
Download binaries from the latest release page and place them in your $PATH.
Install the VSCode extension
The FTL VSCode extension provides error and problem reporting through the language server and includes code snippets for common FTL patterns.
Development
Initialize an FTL project
Once FTL is installed, initialize an FTL project:
ftl init myproject
cd myproject
This will create a new myproject directory containing an ftl-project.toml file, a git repository, and a bin/ directory with Hermit tooling. The Hermit tooling includes the current version of FTL, and language support for go and JVM based languages.
Create a new module
Now that you have an FTL project, create a new module:
- Go
- Kotlin
- Java
- Schema
ftl module new go alice
This will place the code for the new module alice in myproject/alice/alice.go:
package alice
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/block/ftl/go-runtime/ftl" // Import the FTL SDK.
)
//ftl:verb
func Hello(ctx context.Context, name ftl.Option[string]) (string, error) {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hello, %s!", name.Default("anonymous")), nil
}
Each module is its own Go module.
ftl module new kotlin alice
This will create a new Maven pom.xml based project in the directory alice and create new example code in alice/src/main/kotlin/ftl/alice/Alice.kt:
package com.example
import xyz.block.ftl.Export
import xyz.block.ftl.Verb
@Export
@Verb
fun hello(req: String): String = "Hello, $req!"
ftl module new java alice
This will create a new Maven pom.xml based project in the directory alice and create new example code in alice/src/main/java/ftl/alice/Alice.java:
package com.example;
import xyz.block.ftl.Export;
import xyz.block.ftl.Verb;
public class Alice {
@Export
@Verb
public String hello(String request) {
return "Hello, " + request + "!";
}
}
When you create a new module, FTL generates a schema that represents your code. For the examples above, the schema would look like:
module alice {
verb hello(String?) String
}
The schema is automatically generated from your code and represents the structure of your FTL module, including data types, verbs, and their relationships.
Any number of modules can be added to your project, adjacent to each other.
Start the FTL cluster
Start the local FTL development cluster from the command-line:
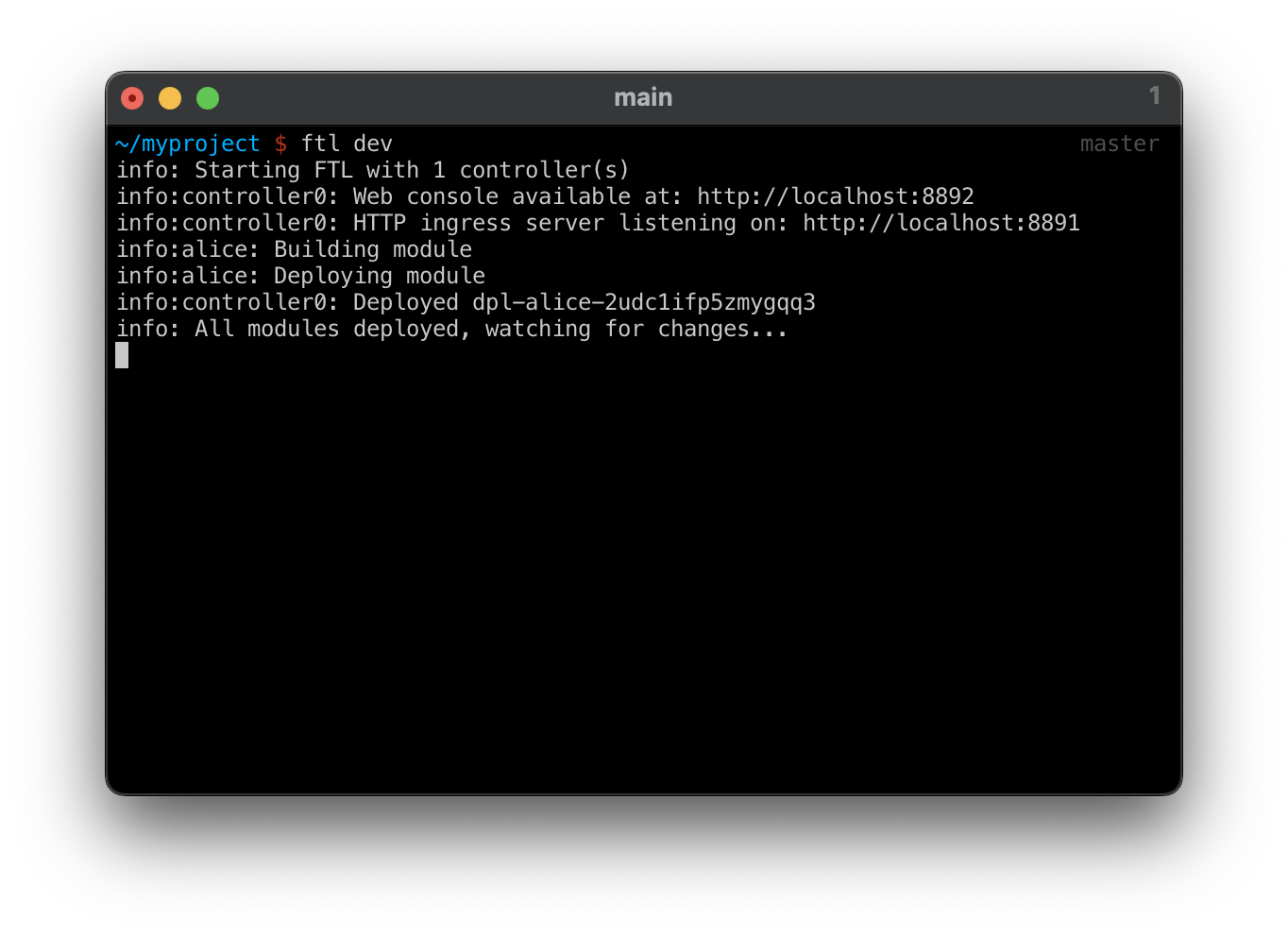
This will build and deploy all local modules. Modifying the code will cause ftl dev to rebuild and redeploy the module.
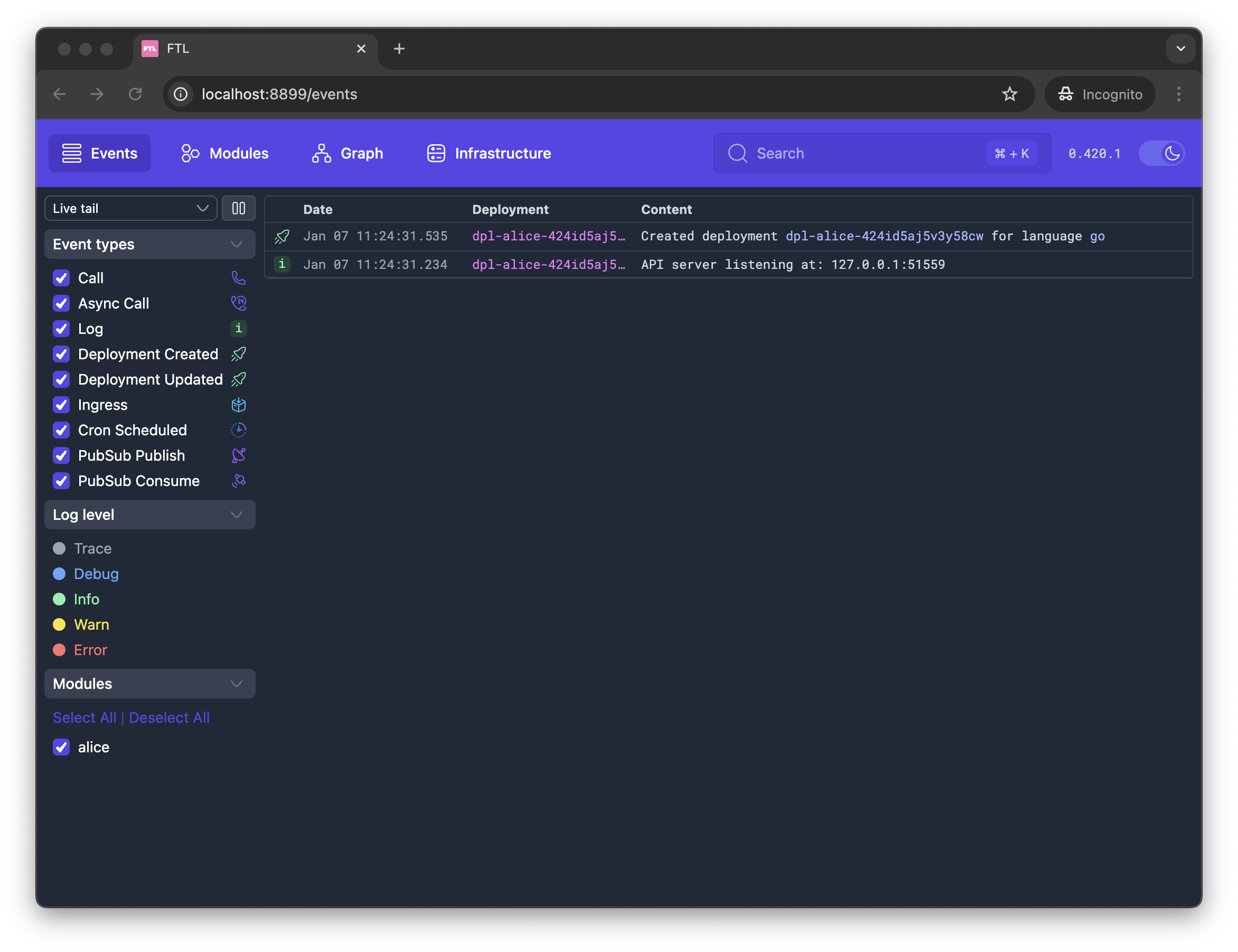
Open the console
FTL has a console that allows interaction with the cluster topology, logs, traces, and more. Open a browser window at http://localhost:8899 to view it:
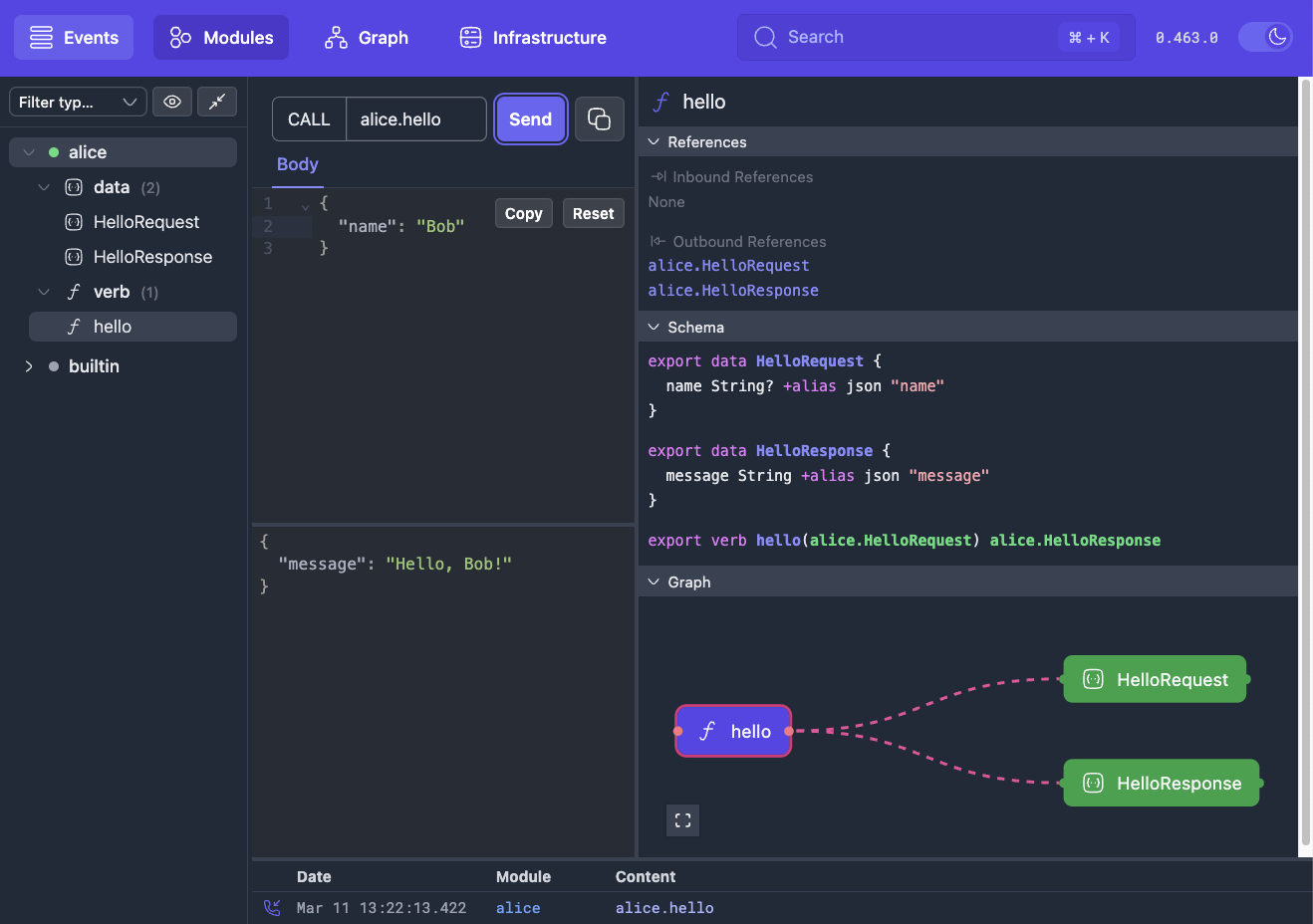
Call your verb
You can call verbs from the console:
Or from a terminal use ftl call to call your verb:
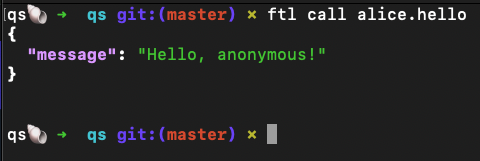
And view your trace in the console:
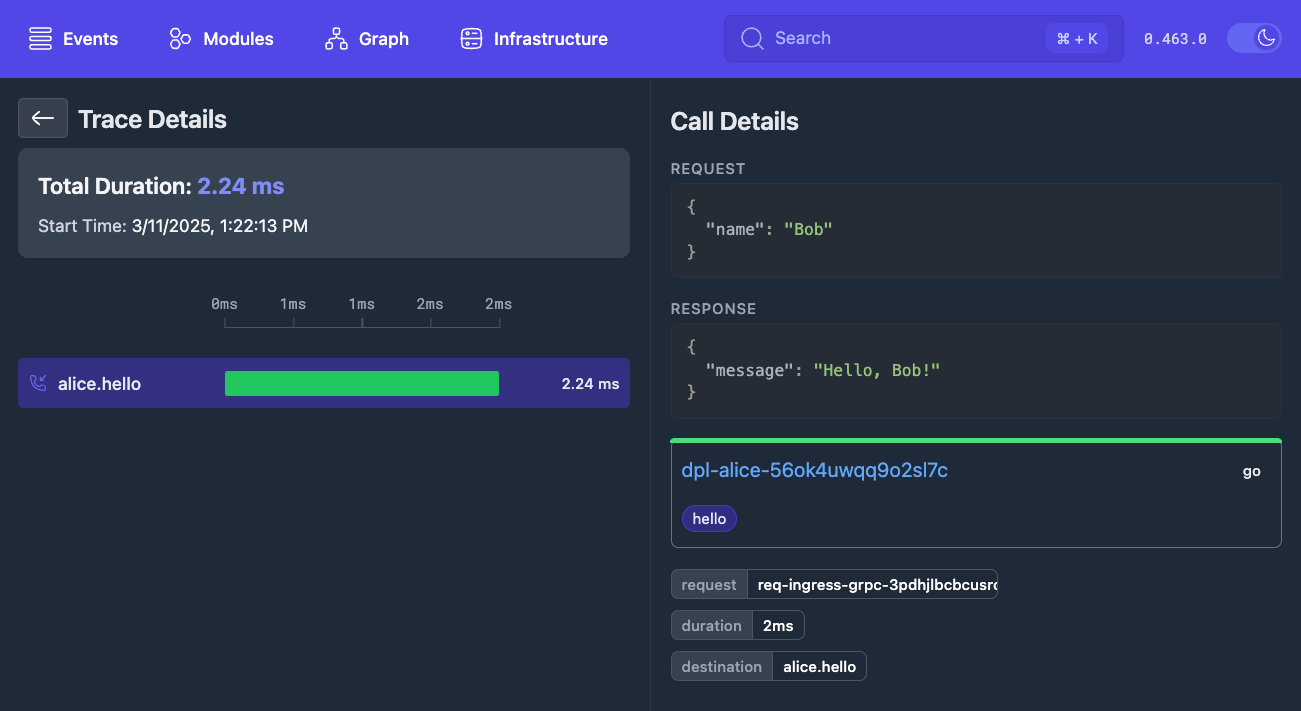
Create another module
Create another module and call alice.hello from it with by importing the alice module and adding the verb client, alice.HelloClient, to the signature of the calling verb. It can be invoked as a function:
- Go
- Kotlin
- Java
- Schema
//ftl:verb
import "ftl/alice"
//ftl:verb
func Other(ctx context.Context, in string, ec alice.HelloClient) (string, error) {
out, err := ec(ctx, in)
...
}
package com.example
import xyz.block.ftl.Export
import xyz.block.ftl.Verb
import ftl.alice.Hellolient
@Export
@Verb
fun other(req: String, hello: HelloClient): String = "Hello from Other , ${hello.call(req)}!"
Note that the HelloClient is generated by FTL and must be imported.
package com.example.client;
import xyz.block.ftl.Export;
import xyz.block.ftl.Verb;
import ftl.alice.HelloClient;
public class OtherVerb {
@Export
@Verb
public String other(String request, HelloClient helloClient) {
return "Hello, " + helloClient.call(request) + "!";
}
}
Note that the HelloClient is generated by FTL and must be imported.
When you create a second module that calls the first one, the schema would look like:
module alice {
export verb hello(String?) String
}
module other {
export verb other(String) String
+calls alice.hello
}
The +calls annotation in the schema indicates that the other verb calls the hello verb from the alice module.